Efficient Mixing and Blending from A to Z
One of the most important properties in Oil-based, Synthetic-based and Invert-Emulsion Drilling Fluids is the electrical stability (ES). ES relates to the stability of the emulsion and oil-wetting capabilities. There are many factors that can affect the degree of emulsification, such as suspended solids, dynamic shear, temperature and pressure. In many cases large volumes of oil-based drilling fluids are mixed without proper and adequate shearing, causing the oil to separate and barite settling.
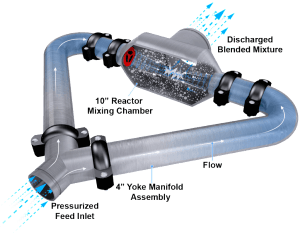
The Chaos Mixer is a mixing device that will assure maximum Electrical Stability. When the drilling fluid passes through the opposing Cavitation Mixing Nozzles and collapse in the mixing chamber due to the sudden reduction in pressure, the forming vapor bubbles implode, generating dynamic shear and fine particle dispersion.
Cavitation Mixing Nozzle:
Hydrodynamic Cavitation is the formation, growth and implosive collapse of developing vapor bubbles in a liquid, created by a fluctuation in fluid pressure. The hydrodynamic process generating the formation, intensity of implosion and speed of collapse can be controlled through feed pressure to produce the necessary energy dissipation levels. In the application of cavitation dispersion for finely dispersed emulsions, 92.4 ft/sec. or 40 PSI is adequate.
The slurry enters the converging section of the Cavitation Mixing Nozzle which increases the velocity to approximately 92.4 ft/sec., the slurry then passes through the throat section of the nozzle, gaining full velocity. As the slurry enters the diverging section of the diffuser the high velocity is suddenly converted into pressure, causing vapor bubbles to form.
Please contact our sales team to learn more about our Chaos Mixer and our Pilot Study Program.
Chaos Mixer Pictures
Applications
Below are some common applications with which we have achieved optimal results. This is not an inclusive list, so if you do not see your specific ingredient listed below, please let us know and we will be glad to discuss it further. Contact Us!
| A – F | G – Pol | Pot – Z |
|---|---|---|
| Ammonium Acetate | Gelatines | Potassium Acetates |
| Ammonium Silicate | Gluten | Potassium Aluminum Silicate |
| Anti-caking Agents | Glycerol | Protein Powders |
| Anti-foaming Agents | Gravies | Resins |
| Barley Flour | Guar Gum | Sodium Acetate |
| Bentonite | Gum Arabic | Sodium Aluminum Phosphate |
| Biopolymers | Hard-to-mix Ingredients | SCMC (Sodium Carboxymethylcellulose) |
| Calcium Bisulfate | HEC (Hydroxy Ethyl Cellulose) | Sodium Citrates |
| Calcium Carbonates | HEMC (Hydroxy Ethyl Methyl Cellulose) | Sodium Gluconate |
| Calcium Citrates | Hydrocolloids | Sorbitan (Emulsifier) |
| Calcium Formate | Hydroxypropyl Cellulose | Sulfuric Acid |
| CMC (Carboxymethylcellulose) | Lime | Starches |
| Carrageenan (Polysaccharides) | Magnesium | Sugar and Sugar Substitutes |
| Caropol | Magnesium Stearate | Tara Gum |
| Citric Acid | Milk Powder | Talc |
| Clays | Mineral Salts | Thickeners |
| EDTA | Oils and Fats | Vegetable Gums |
| Emulsifiers | Pectins | Wheat Flour |
| Flavours | Polymers | Xanthan Gum |
| Flocculants | Polysorbates (Emulsifiers) | Zinc Acetate |
Performance
Please click on the corresponding links below to access a PDF file of our Chaos Mixer Performance Charts
Chaos Mixer
Chaos Mixer Performance chart
To learn how our systems can lower your costs and improve the quality of your products, contact us for more information!